Abstract
Early relapse of newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (ndDLBCL) remains a major clinical problem. Approximately 30-40% of DLBCL patients have early events (progression, relapse, require retreatment, or death) within 24 months of diagnosis (EFS24) and have poor outcomes. Recent genetic and molecular classification of DLBCL has advanced our knowledge of disease biology, yet these classifiers were not designed to predict which cases will have an early relapse and may require more aggressive therapies. Whole exome sequencing (WES) and RNA sequencing (RNAseq) data from ndDLBCL were utilized to identify a signature at diagnosis associated with early clinical failure.
Tumor biopsies from 444 untreated ndDLBCL patients enrolled in the Mayo/Iowa Lymphoma SPORE Molecular Epidemiology Resource (MER) were used for the study along with tumor biopsies from 144 relapsed/refractory DLBCL (rrDLBCL). RNA and DNA were isolated from FFPE tumor samples and analyzed by WES (n=404 ndDLBCL), OncoScan (n=213), and RNAseq (n=321 ndDLBCL, n=144 rrDLBCL). Validation cohorts included BCCA, NCI, and Duke. A combination of weighted gene correlation network analysis (WGCNA) and differential gene expression analysis (DGE) was applied to the RNAseq data. Singscore was used to generate a single score for the WGCNA and the RNA signature associated with EFS24 in the discovery and validation cohorts. Pathway analysis was performed using pathfindR. Genetic classification was done using LymphGen and HMRN. The tumor microenvironment was analyzed using TME26, CIBERSORTx, Lymphoma Microenvironment Classification (LME), and Lymphoma EcoTyper.
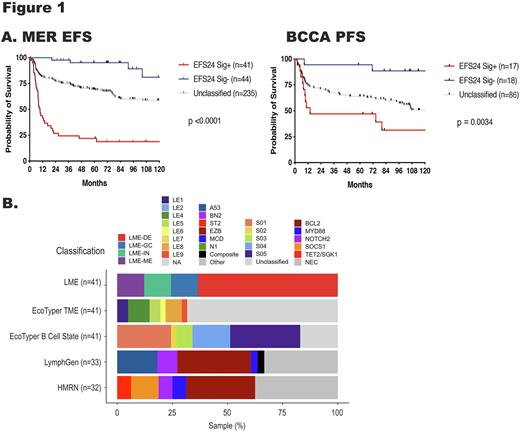
While classifiers that associate with aggressive disease have been reported, none accurately identify most early clinical failures. ABC COO identified aggressive cases in our cohort (40% of EFS24 fail), but also those that achieve EFS24 (29%). While testing for double hit (DHL) captured only 12% of EFS24 failures. Classification of cases by LymphGen, HMRN, LME, and EcoTyper were not significantly associated with EFS24 using Kaplan-Meier analyses. To identify an expression signature that would discriminate EFS24 failures from those that achieve EFS24, a systems biology approach, WGCNA, was used to identify co-expression modules that associate with clinical traits. 15 co-expressed modules were identified, and as expected, modules significantly associated with COO were found. A module encompassing 37 genes associated with EFS24 failure was also identified, and after scoring, the WGCNA signature positive cases were associated with EFS24 failure (p<0.0001). As a secondary approach, we performed DGE analysis comparing EFS24 achieve vs fail and EFS24 achieve vs rrDLBCL patients. Integration of all three analysis identified a gene signature (n=387) that was scored to classify our ndDLBCL cohort into EFS24 signature positive (EFS24 Sig+), negative (EFS24 Sig-), and unclassified. EFS24 Sig+ classification identified 36% of the EFS24 failure cases, Kaplan-Meier analysis showed strong association with continuous EFS in our MER cohort (p<0.0001, Fig. 1A), was significant in both ABC and GCB, and maintained significance after removal of DHL. Furthermore, the classification showed association with PFS in 3 independent cohorts (BCCA shown in Fig. 1A). EFS24 Sig+ tumors enriched for ABC COO, TP53 mutations, BCL2 and BCL6 gains, and encompassed cases across most LymphGen, HMRN, LME, and EcoTyper classifications (Fig.1B) further highlighting that these classifiers do not discriminate EFS24 failures. Classification also identified patients (EFS24 Sig-) who had an extremely good outcome (Fig 1A) and may not require aggressive treatment or consideration for clinical trials. To further understand the biologic underpinning that define EFS24 Sig+ cases, we performed pathways analysis and profiled the TME. The analysis revealed a signature of metabolic reprogramming and TME depletion. Finally, the WES data was integrated into the signature to evaluate an improvement in the ability to predict EFS24 in MER and PFS/OS in validation cohorts. With inclusion of mutations in ARID1A, 45% of EFS24 failure, and only 9% of EFS24 achieved, cases were identified. This novel and integrative approach is the first to identify a signature at diagnosis that will identify DLBCL that will have an early clinical failure and may have significant clinical implications for design of therapeutic options.
Disclosures
Stokes:BMS: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Ortiz:Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Stong:Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Huang:Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Maurer:BMS: Research Funding; Morphosys: Research Funding; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; GenMab: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Roche/Genentech: Research Funding. Link:MEI: Consultancy; Novartis: Research Funding; Jannsen: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Genentech / Roche: Consultancy, Research Funding. Ansell:SeaGen: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Regeneron: Research Funding; Affimed: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding. Nowakowski:Bantam Pharmaceutical: Consultancy; Blueprint Medicines Corporation: Consultancy; Celgene Corporation/Bristol Myers Squibb: Consultancy, Research Funding; Curis, Inc.: Consultancy; Daiichi Sankyo Inc: Consultancy; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Research Funding; Genentech, Inc: Consultancy, Research Funding; Incyte: Consultancy; Karyopharm: Consultancy; Kite Pharma Inc.: Consultancy; Kymera Therapeutics: Consultancy; MorphoSys US Inc: Consultancy; NanoString: Research Funding; Ryvu Therapeutics: Consultancy; Selvita: Consultancy; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy; Zai Lab: Consultancy. Cerhan:BMS/Celgene: Research Funding; Genentech: Research Funding; GenMab: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; NanoString: Research Funding; Protagonist: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Gandhi:Bristol Myers Squibb: Current Employment, Current equity holder in publicly-traded company. Novak:Bristol Myers Squibb: Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal